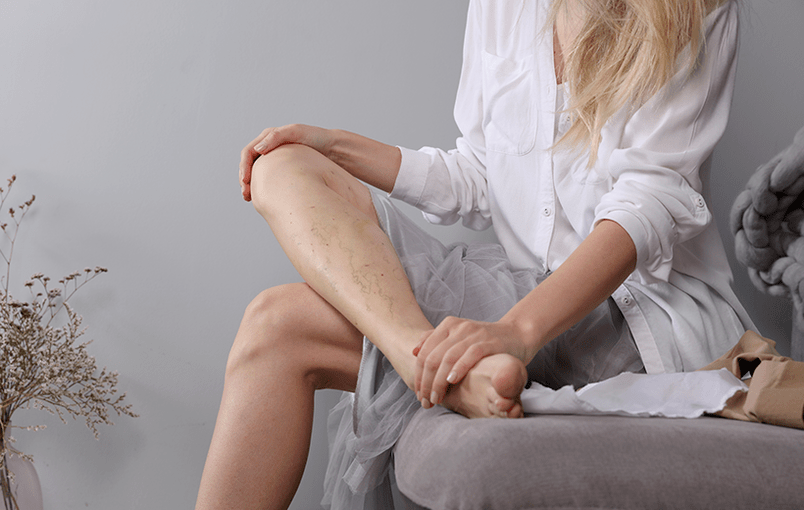
Varicose veins of the legs are one of the most common diseases in the world and, according to the WHO, occur in every fifth person. The pathology of the venous vessels of the lower extremities is associated with the failure of intravenous valves, varicose veins and thinning of their walls. This leads to the reverse flow of blood and its stagnation in the veins. The patient's movements are difficult, pain syndrome occurs, working ability and quality of life are reduced.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities are caused by many factors. Therefore, the disease requires an accurate diagnosis and competent treatment, which is selected individually for each patient.
In the absence of timely therapy, a separate blood clot can lead to dangerous complications, disability, disability, and even death.
Causes of varicose veins
The blood in the veins moves in jerks towards the heart. This is due to the muscles of the lower extremities, as well as intravenous valves that prevent blood flow in the opposite direction. When the valves fail, the blood flows against the movement, the pressure in the veins increases and they expand. As a result, the venous wall becomes thinner, and blood diffuses through it into the surrounding tissues, swelling and pain in the lower extremities appear.
Predisposing factors for varicose veins include:
- heredity;
- excessive load on the lower limbs due to being overweight, intense physical exercise, carrying weights;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- pulling or pinching the veins of the lower extremities (tight clothing, bandages, sports equipment: expanders, elastic bandages);
- long-term and regular work in a sitting or standing position without changing body position and regular rest;
- constant wearing of shoes with heels;
- pregnancy and menopause;
- chronic diseases (constipation, diabetes, kidney and cardiovascular diseases).
In men, the main factors for the development of varicose veins are heredity, unbalanced physical activity and bad habits, while varicose veins in women are more often associated with hormonal changes in pregnancy and menopause, wearing uncomfortable shoes.
Symptoms of varicose veins
The first signs of the disease may not be felt physically, but appear only on the outside in the form of dark blue and purple veins that see through the skin, spider veins and spider veins, bulging veins above the skin surface in the form of twisted cords.
Signs of the next stage of varicose veins are manifested in the form of discomfort and pain, there are pulsations, tingling or cramps in the legs, there are feelings of heaviness and swelling of the lower extremities, itching in the affected area.
Complications of varicose veins
Varicose veins can have serious consequences, cause discomfort and are life-threatening. This includes:
- trophic eczema or skin ulcer in the area of the affected vein, preceded by blanching of the skin;
- deep vein thrombosis caused by a blood clot from smaller superficial veins;
- pulmonary embolism due to blood clots that have entered the bloodstream from the veins of the lower extremities;
- rupture of varicose veins, which is accompanied by profuse bleeding that is difficult to stop.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
Problems with veins are dealt with by phlebologists, but other specialists also participate in making an accurate diagnosis: an angiologist, dermatologist, nutritionist, endocrinologist, and if surgery is needed, a vascular surgeon.
At the initial consultation, the phlebologist explains the symptoms, when they appeared and how often they recur, and also asks if there are similar problems with other family members. In addition, it is important that the doctor knows about the patient's lifestyle and habits.
After a complete examination of the lower extremities and a particularly disturbing area, the phlebologist can refer the patient for additional examinations: ultrasound, phlebography (X-ray of the veins), phlebomanometry (measurement of blood pressure in the veins), three-dimensional computed tomography, phleboscintigraphy (assessment of intravenous blood vessels)radiolabeled albumin).
In advanced stages or with complications, dopplerography (color duplex angioscanning) is considered the most accurate method. It allows you to assess the nature of blood flow, the condition of valves and deep veins, to identify reverse blood flow and the presence of blood clots.
Only an accurate diagnosis will enable the doctor to make an optimal treatment plan.
Treatment of varicose veins
Therapy is aimed at recognizing and minimizing the influence of factors that cause the disease, as well as at eliminating the consequences and preventing complications.
There are three approaches to treating varicose veins: conservative, minimally invasive, and radical surgery.
Conservative treatment of varicose veins includes:
- The use of ointments, gels and tablets based on phlebotonics - substances that improve the tone of the veins, the condition of their walls, blood circulation, relieve swelling and discomfort. An effective drug from this group for varicose veins is Detralex, which includes five herbal components that have a beneficial effect on the condition of venous vessels. The drug is available in two forms: tablets and oral suspension.
- Wearing compression underwear, which creates optimal pressure in the problem areas of the legs, prevents the expansion of veins and maintains the tone of the vascular wall.
- Diet therapy, depending on the specific case, can be aimed at weight loss, strengthening the walls of venous vessels, preventing edema and normalizing stool. It is not only the diet that is important, but also the specific diet, as well as the optimal amount of water consumption.
- Physiotherapy is necessary to improve blood circulation, increase muscle tone and blood vessels in the legs, and eliminate venous congestion. In addition, physical activity helps to normalize body weight and improves the mental state of the patient. Varicose vein sports require safety precautions. In particular, during training, you must wear compression underwear and drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and increase blood viscosity. Prolonged static loads and lifting of heavy loads are also prohibited. After training, it is recommended that you lie on your back with your legs raised to ensure that blood flows from your veins.
Non-invasive methods of removing varicose veins include laser treatment (exposure to laser) and radiofrequency ablation (exposure to high frequency current). As a result, the walls of the vessel are soldered, and the vein soon recedes.
Sclerotherapy is also performed: sclerosant is injected into the affected vein - a special substance that causes its blockage. As a result, blood flow is redirected to the nearest healthy vessel, and the problematic vein disappears over time. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis with the obligatory wearing of compression underwear after it.
In severe cases of varicose veins, phlebectomy is performed - an operation to partially or completely remove a damaged vessel. Such a radical approach is recommended in cases when the patient has contraindications to the methods of "soldering", as well as at high risk of recurrence of the disease.
After the operation, in order to prevent varicose veins in the future, it is necessary to normalize the diet, give up bad habits, take medication prescribed by your doctor to thin the blood and strengthen blood vessels, and perform therapeutic exercises.
Prevention of varicose veins
It includes sports activities (swimming, walking, cycling, light jogging, aerobics), adherence to a drinking regime, avoiding bad habits, tight clothing, high-heeled shoes, regular warm-up during sedentary work, as recommended by a doctor. doctor - wears compression stockings. In addition, it is important to monitor general health in order to identify and treat diseases that can cause varicose veins in a timely manner.
At the first suspicion of a problem with blood vessels, you should consult a specialist for diagnosis and timely start of treatment.